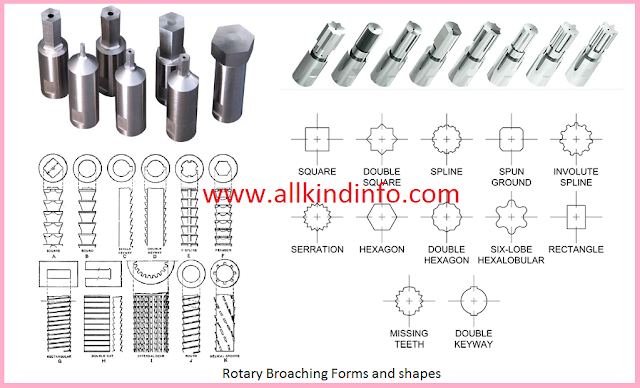
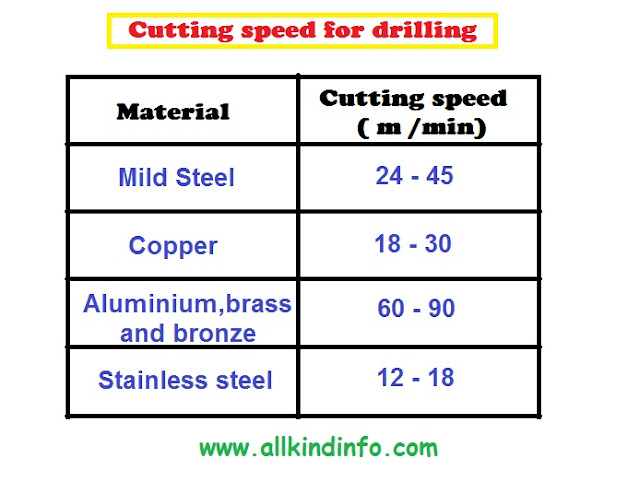
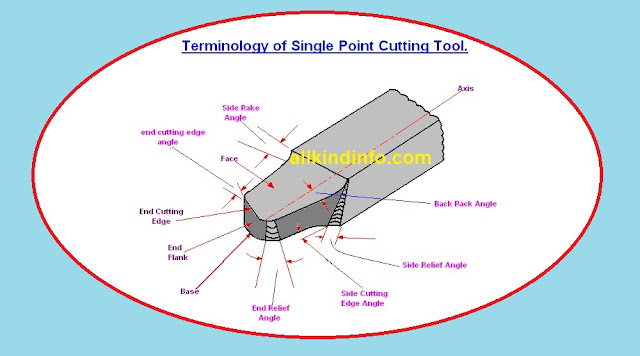
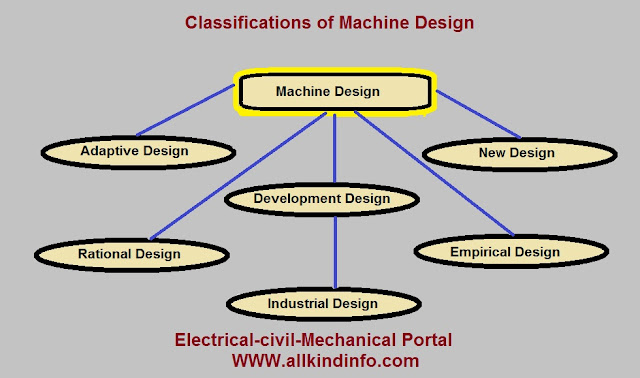
Basic Elements of jigs and fixtures (Body and Locating devices)
Different elements of jigs and fixture are commonly used in the workshop and their uses and functions are as follows.
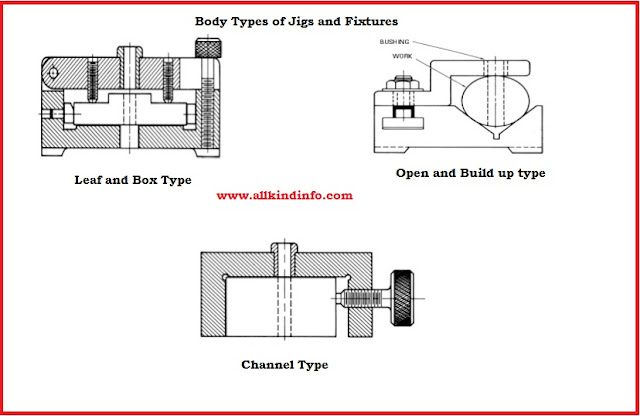
1 : Body
Material of jig body is made from cast iron manufactured through casting or fabrication operations. Body slabs and bars are fabricated by welding and then heat treated to decrease the stresses. Its main function is to support the work piece and hold the job.Different body types of jigs and fixtures are as follows.
(i) Plane Type Body
The most simplest form of body is called plane type body. When holes to be drilled in a simple way this type of body could be used. Drilling operation can be performed without or with the guide bushes.
(ii) Channel Type Body
This type of body contains a channel or more than two channels. Channel are made from steel and Cast Iron materials.
(iii) Box Type Body
When many holes are required from different sides. Template plates can be used to drill from any plane.One side of the box is mounted with a lid, which is helpful for loading and unloading the job.
(iv) Built Up Type Body
Dowels, screws and locating pins are used in this type of body. Material of this body is a standard steel. Blocks are used to locate and position the job.
(v) Leaf Type Body
This is the most advanced and modified type of body. A fulcrum type lid is adjusted on the top of the body.It is used in case of measured large work pieces where it may necessary to hold the whole component in the jig.
2: Locating Devices.
Different types of pins are used to locate the component in the jigs and fixtures body. These pins are made from hardened steel. Shank or neck of the pin is press fitted into the jigs and fixtures body.Various types of locating pins are.
(i) Support Locating Pins
These are also called rest pins, which are used to adjust the work piece. Support locating pins have two kinds. First type is called fixed type, which are used to locate the face either round, curved or flat. Spherical or round head insure stable locating.Second type of pins are adjustable type, which are used where dimension of work piece can vary. These are mostly used in forging,sand casting.
(ii) Locating Pins
When Finished holes or reaming is required then these pin are used. These pin are also used to locate the work piece as well. Conical and cylindrical types of locating pins are used in the work shop.
(iii) Jack Pins
These pins are also called spring pins. Purpose of these pins are to locate the job whose length is subject to variation. Spring allows the compression and locate the work piece easily. Locking screw type of jack pin is more secure when job is adjusted and then pin can lock whole face of the work piece.