Electric Charge
Electric charge, basic property of matter carried by some elementary particles. Electric charge, which can be positive or negative, occurs in discrete natural units and is neither created nor destroyed.
Current.
Current is defined As current motion involving charge via a conducting material. The unit involving current will be ampere while charge will be measured throughout Coulombs.
It can also be described as movement of electricity along a conductor.
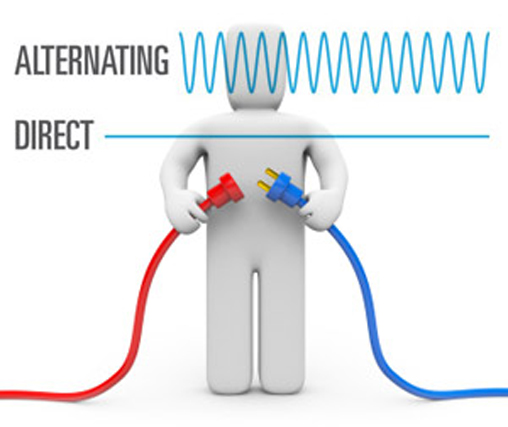
Direct Current (D.C.)
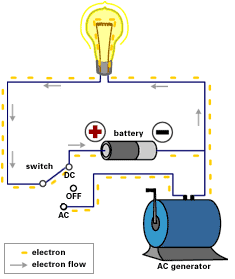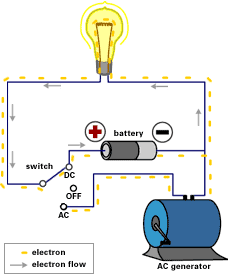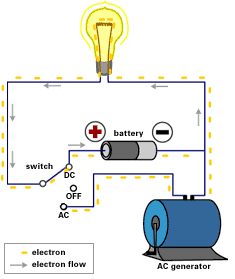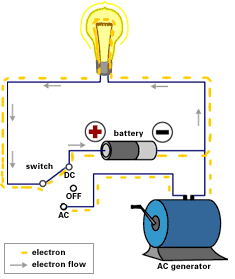
Direct current or constant current is actually many commonly found throughout homes in the application regarding electrical energy kept inside batteries. with a great DC circuit, The sort of voltage along with the direction of application are generally constant. The level of voltage is usually determined through the type in addition to size regarding battery. ones direction involving current flow is additionally constant and, Just as inside AC circuits, The sort of current flow is determined by the fill up resistance.
Batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy. chemical energy is actually within wet form, Equally Utilizing your car battery, as well as within dry application Equally in flashlight in addition to transistor-radio batteries. several batteries are generally made to possibly be recharged via a AC source. Voltage via almost all batteries, unless recharged, will gradually decrease. AC power is actually converted for you to DC power pertaining to a few functionalities for the home. Your own conversion is actually done by a good device called the rectifier or perhaps current converter.
Alternative Current. (A.C.)
Alternative current or time varying current can be defined as a flow of electrons that will reverses it is direction involving flow at regular intervals with the conductor.
Ampere.
The basic SI unit of measuring the quantity of electricity.
The range connected with whole charge The item passes in the course of a great arbitrary cross section of a conducting material per unit second will be defined just as one Ampere.
Mathematically
I = Q/t or Q = I.t
Where
Q is symbol of charge in coulombs,(C)
I is the current in amperes (A)
t is the time in second (s)
Voltage or Potential difference.
Voltage attempts to Produce a current flow, as well as current may flow no matter whether ones circuit can be complete. Voltage will be sometimes stated just like the 'push' or 'force' of electricity, it isn't really a force but this may help you to imagine what is happening. It is possible to have voltage without current, but current cannot flow without voltage.
Volt
A unit involving electrical pressure (or electromotive force) of which causes current to be able to flow with the circuit. individual volt is usually The level of pressure necessary to cause one ampere of current to be able to flow against one ohm regarding resistance.
Watt.
A unit involving measure with regard to indicating ones electrical power applied with a great circuit. This really is taken coming from multiplying the current (in amperes) by the electrical pressure (in volts) in which cause That for you to flow. watts = amperes x volts.


Post a Comment